Cultivated Meat (Cell-Based Meat) Market Research
Meat production has been under the spotlight for its ethical issues and environmental impact for years. Acres of land are dedicated to raising cattle and livestock, which can affect agricultural production and land fertility.
Consequently, the market introduced Cultivated or Cell-based Meat to create changes and introduce new improvements in the meat industry. However, the Cultivated Meat Market received a mixed reaction from meat producers and consumers.
Although with a rocky start, this market is expected to grow in the coming years as it gathers more interest with the promise of producing meat and other proteins with minimal resources needed and lesser chances of getting foodborne illnesses.
What is Cultivated Meat?
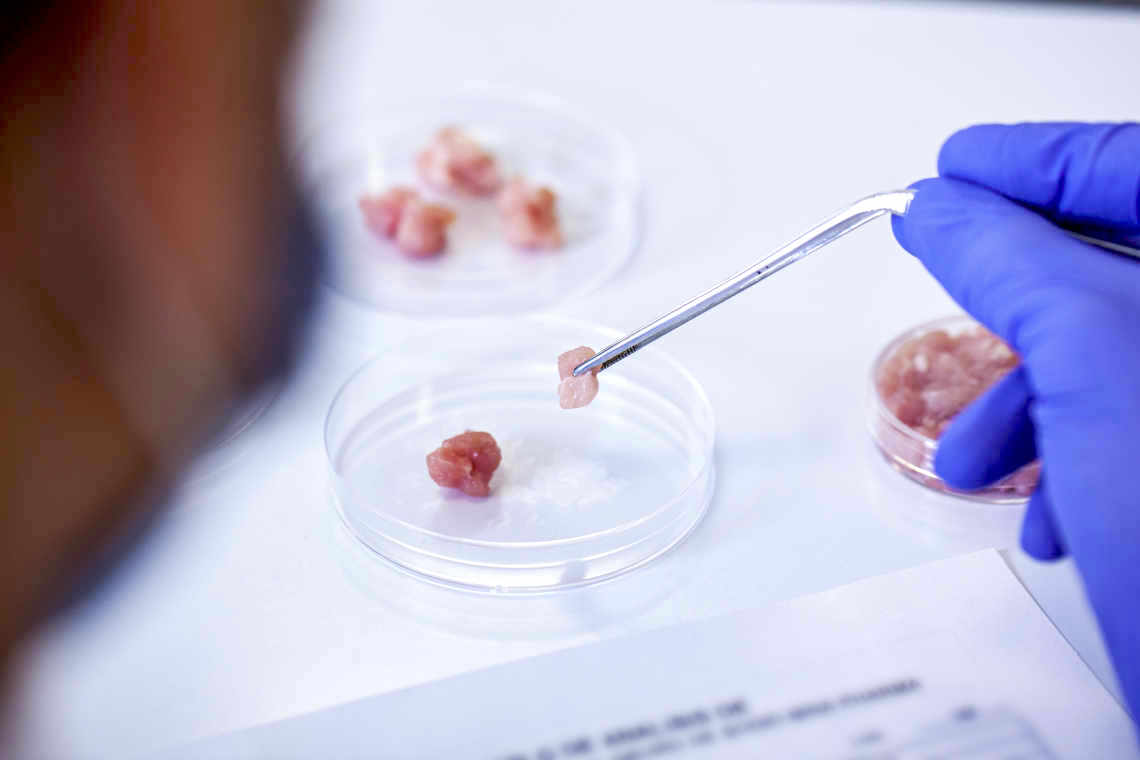
Cultivated Meat, also known as Cell-based Meat, is produced by directly cultivating animal cells to produce real animal meat and other proteins. Cells used come from animal stem cells, which are then arranged similarly to the animal’s tissue.
This arrangement allows for the Cultivated Meat to retain the texture, taste, and nutritional value of a regular animal protein. Companies and laboratories successfully re-create proteins from different animals, ensuring wider selection for public consumption.
Benefits of Cultivated Meat Market Research
The Cultivated Meat Market falls under the gray area of the food industry as lab-grown protein is highly unusual. This is where Cultivated Meat Market Research comes in to provide insightful data and information for investors to determine the feasibility of the market.
Basically, it benefits these entrepreneurs by helping them understand how the Cultivated Meat Market works and how it can adapt in every place, factoring in the consumers, the environment, and the policies imposed. To further explain, here is a breakdown of the benefits a Cultivated Meat Market Research has:
- Discover whether there is a demand in the area – Lab-grown protein is considered taboo in many countries. Having dedicated research to establish whether people are eager or opposed to Cultivated Meat can help investors determine if there is an actual demand.
- Government policies that may or may not intervene with the introduction of the Cultivated Meat Market – The Cultivated Meat Market research allows investors to have insight into government policies that may restrict or ban cell-based meat production and sale within their respective territories.
- Thorough understanding of Cultivated Meat and its market – Investors might be reluctant to enter the Cultivated Meat Market because it is an uncommon niche segment of the food industry. The research will help explain and clarify information that investors might want to know.
- Determine the appropriate marketing strategies – The research is instrumental in guiding entrepreneurs in targeting their audience and effective steps to reach out to them while mitigating any possible mistake.
- Check the market competition – The research helps determine the standing of each competitor in the market, which allows investors better position themselves.
Trends and Opportunities in the Cultivated Meat Market
The landscape of the food industry keeps on changing with the introduction of new products, technology, and methodology. It influences the rise and fall of the key players, so it is essential for businesses to keep abreast of any development and changes in the market.
- The Cultivated Meat Market is anticipated to grow as companies and laboratories look forward to commercially mass-producing cell-based proteins.
- Singapore was the first country to approve Cultivated Meat for commercial sale, accessible to the public to purchase. The first restaurant to serve Cultivated Meat, the 1880 restaurant, is also located in Singapore. It is expected that other restaurants will follow suit with the integration of cell-based protein on their menu.
- The Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) cleared and approved Cultivated Meat for human consumption, explaining that it is safely made in a controlled environment. The cultivation of lab-grown proteins was said to be similar to brewing beer.
- Generally, lab-grown proteins are healthier and safer. As it is made of stem cells, there are no internal organs. It means that the Cultivated Meat prevents any cross-contamination, which sometimes happens when butchering meat. No fattening agents or growth hormones are injected, which are common practices in some cattle and livestock farms.
- With FDA greenlighting the Cultivated Meat for human consumption, businesses are more keen to produce better, opening new career opportunities for talented scientists and contributors. Interestingly, it can also boost the demand for food scientists and chefs to find ways to mimic the taste, texture, and aroma of the actual animal protein.
- The Cultivated Meat Market intends to cover as much animal protein as possible, including seafood. It also aims to cater to demographics who do not consume meat.
- Cultivated Meat requires lesser energy and resources to produce. Consequently, it also means that it emits fewer greenhouse gasses in comparison to traditional meat, making it more a sustainable way to harvest animal protein.
Challenges of the Cultivated Meat Market
Despite all the opportunities present in the market, there are some challenges attached to it. Most of the issues often relate to the meat itself, raising questions about its authenticity as animal meat, its production, and the consequences of its availability to the public.
Hence, the market is expected to face the following challenges:
- Non-competitive Pricing: Cultivated Meat requires scientists and specialized tools to produce it, which means higher manufacturing costs. But, there are proposals presented for decreasing the cost of Cell-based meat. One is reducing the growth factor and recombinant proteins by replacing them with plant-based alternatives and fungi.
- Slow Production: Unlike traditional livestock, producing Cultivated Meat includes bioprocess that requires technical skills to complete the animal protein. This process makes meat production tedious and unavailable for mass production. Some scientists and investors team up to conduct studies and experiments to increase production capacity while retaining the Cultivated Meat’s quality.
- Sourcing raw material for each animal protein: No animal meat tastes the same, so the challenge is to find the appropriate raw materials to incorporate for each stem cell.
- The criticism of Cultivated Meat: There are many opinions as to the existence of Cell-based meat and its role as a replacement or alternative for animal protein. Some voice strong opposition to it, claiming different reasons from it being unnatural and against nature to questionable ethics of using stem cells to create protein.

